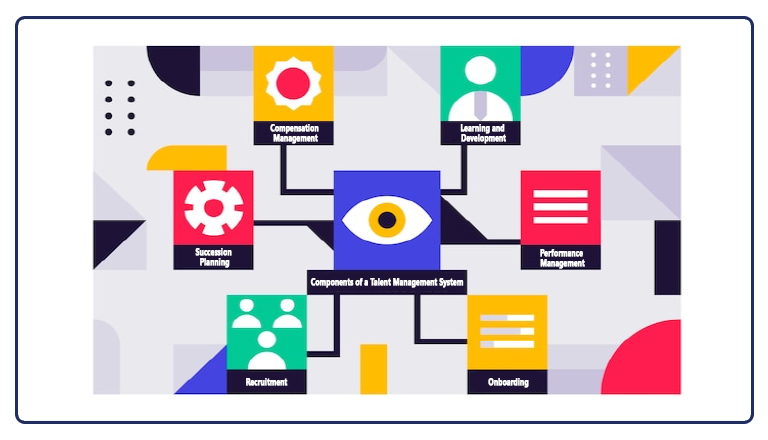
According to Manpower Group, a whopping 75% of organizations globally face challenges filling roles. And, this is just the tip of the iceberg. By 2030, Korn Ferry estimates that the number of unfilled jobs may reach 85.2 million worldwide. This staggering statistic is exacerbated by an increasing employee global attrition rate that has almost doubled between 2013 and 2021.
With these facts in mind, organizations need to do everything possible to attract, retain, and motivate the best talent. Here we share with you the top seven mistakes that organizations make with talent management and how you can avoid them.
Mistake 1: Hiring with only the beginning in mind
Faced with hiring time crunches and the constant need to deliver results fast, hiring managers and HR professionals often scramble to find the best fit for open organizational vacancies. In an attempt to get results fast, there is no better hire than one with the exact education and experience a manager is looking for, often, preferably, experience in the same industry.
As tempting as this is, beware! Your new hires today are the leaders of tomorrow. You must not hire only for the capabilities the candidates demonstrate for the open roles. You must also weigh in their potential for future managerial and leadership roles in your organization.
Moreover, experience is only one side of the coin; exposure is another. Ask yourself, would it help if you hire a candidate with relevant experience from a different industry? Would their exposure expand the organizational viewpoint and open a whole new realm of solutions?
Mistake 2: Bulking experience instead of chunking skills
Organizations often make the mistake of hiring people based on experience, developing individuals based on roles, and promoting talent based on overall performance. As reasonable as this is, there is a catch, past performance is not necessarily an accurate indicator of future performance.
In an increasingly changing world, the experience gained yesterday may prove irrelevant for future roles and organizational demands. Moreover, since it is estimated that 44% of workers’ skills will be disrupted in the next five years due to rapid technological change, organizations are better off chunking employees’ and candidates’ capabilities on a skill-by-skill basis, rather than experience.
Use skills-based or competency-based assessments to assess candidates, employ skills benchmarking to develop individual personalized development plans, and use skills matching to identify possible promotion opportunities for individuals that may on the surface seem far removed from their original area of expertise, but may, in fact, have many skills in common.
Mistake 3: Training at all the wrong times
Timing is one of the most critical factors of training effectiveness. A common mistake that organizations often make is to provide training to employees based on their current roles, with little training investment in potential future roles these employees could play. This leaves organizations usually playing catch-up in training, rather than promoting employees who are already trained and skill-ready for their new roles.
Another common timing mistake is tied to the misconception of day-long in-class training programs. Although these kinds of training programs are effective, organizations must still account for the timing of when information is needed, the regular pace at which learning needs to be reinforced, and the time employees have available for learning. In fact, in our learning and development in the UAE guide, we discovered that 77% of employees surveyed reported not having the time available for learning, making it the number one challenge facing corporate learning today.
To overcome these timing issues, organizations must consider just-in-time learning by integrating AI into already-used organizational tools and systems. They must also consider self-paced and microlearning options.

Mistake 4: Measuring performance instead of transforming performance
A common mistake organizations make with performance management systems is that they reduce it to simply a ‘system’. This mindset leads organizations to be hooked on setting objectives, filling in appraisal forms, and doing it all over again the following year. This kind of mindset often leaves actual current performance out of the equation and leaves employees feeling disenchanted.
To overcome this issue, organizations need to approach performance management with a culture-first mindset. Performance management, in its essence, is not about setting annual objectives, but rather about providing a compass to guide everyone in the organization.
It is also about checking in often daily or weekly about how well we all measure to that compass. Organizations that truly embrace performance management are more in the now, than in the past, and leverage their technologies and systems to keep everyone motivated towards the North Star metric.
Mistake 5: Really boxing people in the 9-box grid
First introduced by McKinsey in 2008, the 9-box grid scoring people across two dimensions, performance and potential, has quickly become one of the most commonly used talent identification and succession planning tools in organizations worldwide. The tool places employees in one of nine boxes such as rising star, key contributor, adequate performer, etc., and is often used to identify individuals more suitable for promotions and growth opportunities.
One of the biggest mistakes organizations make is to actually ‘box’ people based on the grid. Organizations must be aware that all employees deserve growth opportunities, each according to their own growing potential and increasing performance. The key here is that the grid does not tell you where someone ‘can be’ in the future; it only tells you whether they are ‘ready now’. Human potential is ever-expanding and should never be limited.

Mistake 6: Thinking pay instead of benefits
Some organizations consider higher pay as a means to retain and motivate talent. As significant as pay is, it is still not the only way to retain your organizational talent. Employees look at the overall compensation and benefits packages when making career move decisions. These benefits could include traditionally-known benefits such as medical insurance, social insurance, and incentives. But you can also consider more modern benefits such as work-from-home options, flex hours, daycare in-house, free e-learning platform access, profit share, recognition awards, mentoring and coaching programs, gym access, and even free coffee and snacks.
Mistake 7: Managing by attendance instead of managing by objectives
Talent management systems often come with a core HR & payroll module. They provide a great edge in automating attendance tracking, leave calculations, and payroll management. Although they enhance HR efficiency helping you focus more on the actual HR work that matters, you must not fall for the temptation of making these systems serve as a measure of employee commitment.
Attendance does not equal productivity. In fact, Stanford University research has found that productivity per hour declines sharply when people work more than 50 hours a week. After 55 hours, productivity drops so much that putting in any more hours is pointless. And, those who work 70 hours a week only get the same amount of work done as those who put in 55 hours. That being said, use these attendance tracking systems to make payroll calculations easier and faster, and measure commitment by objectives achievement instead.
Use a State-of-the-Art Talent Management System to Do It Right
These were the top seven fatal mistakes organizations make with talent management. If you’d like to do talent management right, all while saving time, cost, and effort, explore our state-of-the-art talent management solutions. And, if you’d like to know more about the future of talent management, check out our blog article on the 2023 top talent management trends.